Automatically Start and Stop AWS ECS Services via Github Actions
As we wrapped up the Plog (“Blogging project for developers”) deployed on AWS ECS, I wanted a way to variably manage server maintenance costs.
(This project was started for educational purposes, not to maintain a service for profit, so saving money is a priority..)
Though ECS costs were not significant, I still thought it was unnecessary to maintain it aimlessly. However, to ensure that team members can use it as a portfolio whenever they’re transitioning jobs, I planned to devise a way to start up and shut down the API servers.
How to Stop the ECS Service?
It’s actually quite simple. You just need to set the desired number of tasks for the ECS service to 0. Conversely, to start, set the desired number of tasks to the desired number of containers.
Note that this method does not represent a deployment process. It refers to stopping and restarting already running containers.
AWS CLI
Initially, I intended to automate using AWS CLI commands. Although I knew how, I eventually opted to use Github Action for the following reasons:
- Front-end team members were not very familiar with AWS.
- Using AWS Client commands requires AWS Access Key and Secret Key sharing among team members, which didn’t seem elegant.
Steps
- Share AWS Access Key ID and AWS Secret Access Key among team members and install AWS CLI.
- Complete settings by entering the Access Key and Secret Key through AWS Configure.
$ aws configure > AWS Access Key ID [None]: {AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID} > AWS Secret Access Key [None]: {AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY} > Default region name [None]: {AWS_REGION} > Default output format [None]: {AWS_OUTPUT_FORMAT} - Start and stop ECS services via the AWS Client.
$ aws ecs update-service --cluster plog-cluster --service plog-service --desired-count 0 # Stop service $ aws ecs update-service --cluster plog-cluster --service plog-service --desired-count desired task number # Start service
Github Actions
Github Actions is a CI/CD service provided by Github. You can compose CI/CD using various actions provided by Github.
One powerful advantage is Github Secrets, a secret key management system provided by Github. When deploying through Github Actions, secret keys saved in Github Secrets can be used.
Using this feature, I could register and utilize AWS Access Key and Secret Key via Github Secrets without directly inputting them into Github Actions.
Steps
Register AWS Access Key and Secret Key in Github Secrets. a. Go to Github Repository > Settings > Secrets > New repository secret to register
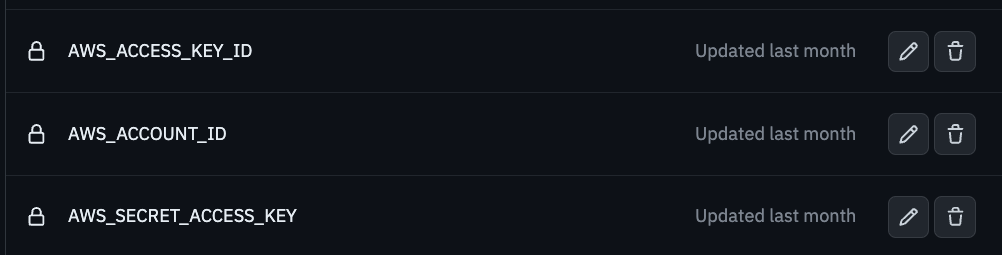
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_IDandAWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY. I also registeredAWS_ACCOUNT_IDsince it is included in the ECR address during ECS deployment.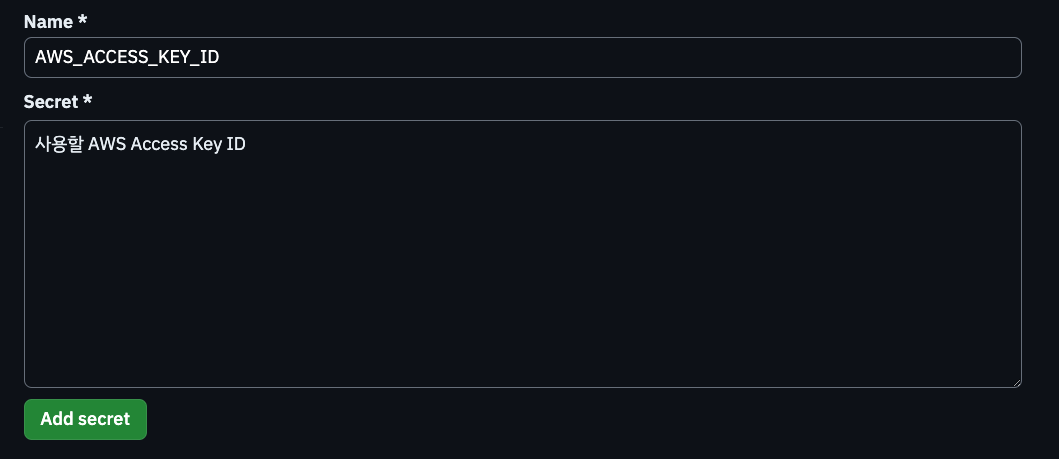
Create an ECS service start workflow file
project-root/.github/workflows/start-ecs.yamlname: Start ECS Service on: workflow_dispatch: env: ECS_CLUSTER: The name of the created ECS cluster ECS_SERVICE: The name of the created ECS service jobs: start-plog: runs-on: ubuntu-latest steps: - name: Checkout uses: actions/checkout@v2 - name: Start ECS Service run: | aws ecs update-service --cluster ${% raw %}{{ env.ECS_CLUSTER }}{% endraw %} --service ${% raw %}{{ env.ECS_SERVICE }}{% endraw %} --desired-count 1 env: AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID: ${% raw %}{{ secrets.AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID }}{% endraw %} AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY: ${% raw %}{{ secrets.AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY }}{% endraw %} AWS_DEFAULT_REGION: "AWS region"Create an ECS service stop workflow file
project-root/.github/workflows/stop-ecs.yamlname: Stop ECS Service on: workflow_dispatch: env: ECS_CLUSTER: The name of the created ECS cluster ECS_SERVICE: The name of the created ECS service jobs: stop-plog: runs-on: ubuntu-latest steps: - name: Checkout uses: actions/checkout@v2 - name: Start ECS Service run: | aws ecs update-service --cluster ${% raw %}{{ env.ECS_CLUSTER }}{% endraw %} --service ${% raw %}{{ env.ECS_SERVICE }}{% endraw %} --desired-count 0 env: AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID: ${% raw %}{{ secrets.AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID }}{% endraw %} AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY: ${% raw %}{{ secrets.AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY }}{% endraw %} AWS_DEFAULT_REGION: "AWS region"
Both actions are the same except for the desired-count. desired-count refers to the desired number of tasks. Setting it to 0 will stop the service, and 1 will start it.
You can see a necessary change in one place in the photo below. ECS adjusts the number of containers according to the specified number of tasks.

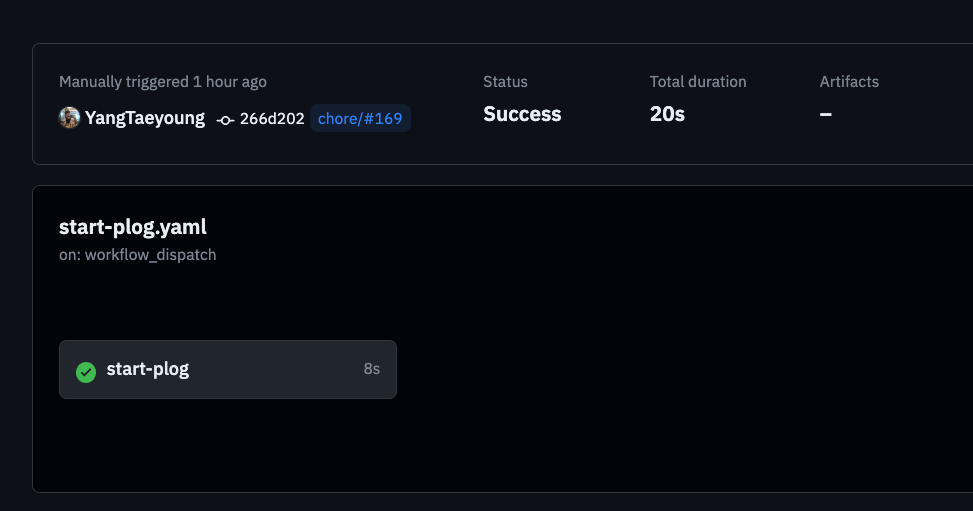
The reason for setting on to workflow_dispatch in each yaml file is to execute Github Actions manually.
Setting the name appropriately makes it look good in the actions list.
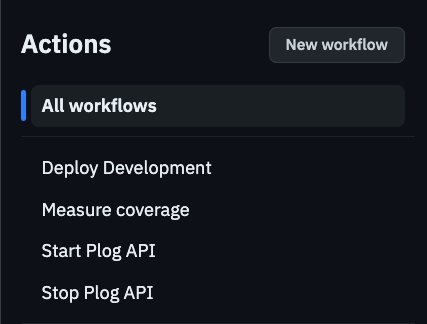
Summary
We explored how to start and stop ECS services through Github Action. Deploying AWS ECS via Github Actions will be discussed later.